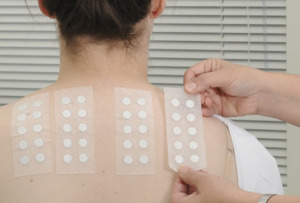
Patch testing is a process used to diagnose allergic contact dermatitis (a Type 4 delayed type hypersensitivity reaction). Allergic contact dermatitis (ACD) occurs when a person becomes allergic to something that is coming into contact with their skin, causing a rash. During patch testing, small amounts of chemicals or products that are used at work or home are diluted and placed onto discs mounted on hypoallergenic tape and then placed on the back of the patient. These are left on the back for 2 days and then removed. The patch tests are “read” by a dermatologist at 2 days, and again at 4-7 days after the patch tests were originally applied. A positive patch test causes a small itchy red mark that is still present at the second patch test reading, and is used in conjunction with the patient history and relevant exposures, to make a diagnosis of ACD.