About dermatitis
Contact dermatitis is a skin condition, which appears similar to eczema. Sometimes people use words ‘eczema’ and ‘dermatitis’ to mean the same thing, but they are different. Contact dermatitis is an inflammatory skin condition caused by external substances touching the skin. Occupational contact dermatitis means that the dermatitis is caused by something you are contacting at work.
Contact dermatitis usually affects the hands, because it is the hands that are most commonly touching substances or products while you work. But it can also affect the arms, face or legs, in fact any part of the body.
Skin dryness is usually the first sign of dermatitis and often starts in the web spaces between the fingers.
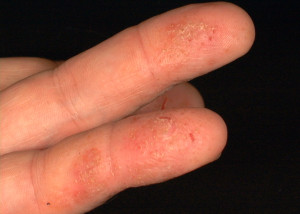
Dermatitis can make the skin:
- Dry
- Itchy
- Red
- Split and crack
- Flake and peel
- Burn and sting
- Develop small blisters
Like eczema, contact dermatitis can be very distressing and unsightly, and people often find the appearance of their skin embarrassing. It can interfere with sleeping, especially when it is very itchy. In some circumstances, dermatitis can become so severe that some people have to give up their job or career. However, it can often be managed with appropriate treatment and good skin care.
When dermatitis develops the skin may take months to heal, even once it looks like it has returned to normal.
Dermatitis commonly affects people working in a range of industries, but most often affects those working in:
- Hairdressing
- Healthcare
- Food handling
- Manufacturing
- Construction
- Printing
- Metal working
- Automotive industry
There are 3 main types of dermatitis:
- Irritant contact dermatitis
- Allergic contact dermatitis
Contact urticaria. This includes latex allergy, which is a type of contact urticaria.
